19 06 2017
ITIL Foundations
If you are in IT, it’s likely you have heard of ITIL (eye-till) certification. According to Wiki, this is: ITIL, formally an acronym for Information Technology Infrastructure Library, is a set of detailed practices for IT service management (ITSM) that focuses on aligning IT services with the needs of business. In its current form (known as ITIL 2011), ITIL is published as a series of five core volumes, each of which covers a different ITSM lifecycle stage. Although ITIL underpins ISO/IEC 20000 (previously BS 15000), the International Service Management Standard for IT service management, there are some differences between the ISO 20000 standard and the ITIL framework.
ITIL describes processes, procedures, tasks, and checklists which are not organization-specific, but can be applied by an organization for establishing integration with the organization’s strategy, delivering value, and maintaining a minimum level of competency. It allows the organization to establish a baseline from which it can plan, implement, and measure. It is used to demonstrate compliance and to measure improvement.
Since July 2013, ITIL has been owned by AXELOS, a joint venture between Capita and the Cabinet Office. AXELOS licenses organisations to use the ITIL intellectual property, accredits licensed examination institutes, and manages updates to the framework. Organizations that wish to implement ITIL internally do not require this license.
Several months ago, I took a class at Lynda.com on ITIL, this class experience was awful. Then I found a course at Udemy on ITIL.
ITIL best practices for Service Management and a library of five books covering lifecycle phases.
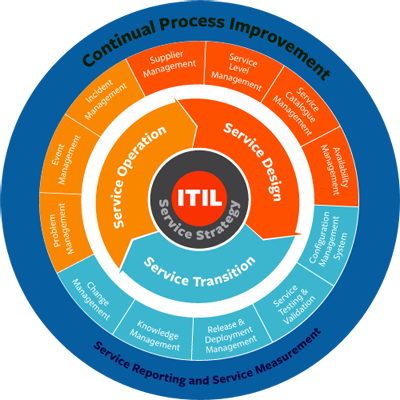
Service Life Cycle (ITIL Core)
- Service Strategy – The Service Strategy. Its focus is on developing the capacity to achieve and maintain a strategic advantage to refine and create policies, guidelines, and processes that cross all of the ITIL service life cycle.
- Processes
- Value creation
- Business case
- Service Design – Takes the Service Strategy, and creates the design that will eventually operationalize those business objectives. The focus is on the design for new changed and updated services. We’re putting in a new service in. We’re retiring a service. We’re changing something about it.
- Processes
- 5 aspects of service design
- RACI, SDP 4P of Services design
- Service Transition – Provides the guidelines for development and improvement of capabilities for transitioning new and changed services into the life service operation.
- Processes
- SMKS, CMS
- Manage risk, complexity
- Service Operation – Manages the day-to-day operation of a service and provides guidelines on the effective and efficient delivery and support.
- Processes and functions
- Communication
- Continual Service Improvement – Provides critical guidelines in creating and maintaining value for customers through better design transition and operation of services. As a former CIO for a large data center operation, we always, we’re looking at our list of services with our portfolio.
- Process
- CSI Register
- PDCA model
- CSI model
- Baselines
- Types of metrics
- Measurement system
All phases have interactions with each other.
Comments are currently closed.